When your cast iron boiler stops delivering consistent heat during winter’s coldest nights, you quickly realize how vital proper maintenance is to your home’s comfort and safety. Cast iron boilers represent some of the most durable heating systems available, with many units lasting 30 years or more when properly cared for. Yet without regular attention to critical components, even these robust systems can develop dangerous issues ranging from inefficient operation to potential carbon monoxide leaks. This guide provides essential maintenance practices that homeowners can safely perform while recognizing when to call a professional—keeping your cast iron boiler operating efficiently for years to come.
Annual Professional Inspection Requirements
Why Licensed Technicians Must Handle Internal Components
Cast iron boilers contain complex combustion systems that require specialized knowledge to inspect safely. Only licensed HVAC professionals should examine burners, heat exchangers, and flue passages due to the risk of carbon monoxide exposure. During an annual inspection, technicians verify proper gas pressure, check for cracks in cast iron sections, and ensure adequate draft in the chimney system—critical safety checks beyond homeowner capabilities.
What to Expect During a Professional Service Visit
Your technician will typically perform these essential checks:
– Combustion analysis to verify proper fuel-to-air ratios
– Flue gas testing for dangerous carbon monoxide levels
– Pressure relief valve verification to prevent dangerous over-pressurization
– Cast iron section inspection for hairline cracks that could lead to leaks
– Water quality assessment to prevent internal corrosion
Schedule professional maintenance every fall before heating season begins. This timing ensures any issues are addressed before you depend on your system during cold weather.
Safe Homeowner Maintenance Tasks
Visual Inspection Protocol for Homeowners
You can safely monitor your boiler’s condition with regular visual checks. Look for these warning signs monthly during heating season:
- Water leaks around piping connections or base of the unit
- Rust accumulation on boiler surfaces or nearby walls
- Unusual noises like banging, whistling, or rumbling during operation
- Soot buildup around burner access panels
- Strange odors when the system activates
Document your observations and share them with your technician during service visits.
Pressure Gauge Monitoring
Your boiler’s pressure gauge should read between 12-15 PSI when the system is cold. Higher pressure indicates potential problems:
- Over 20 PSI when cold: Signals automatic water feeder issues
- Dropping pressure weekly: Suggests undetected leaks in the system
- Spiking during operation: May indicate failing expansion tank
Mark your current pressure reading with a marker when the system is cold. Check it monthly to identify developing issues early.
Water Treatment and Quality Management
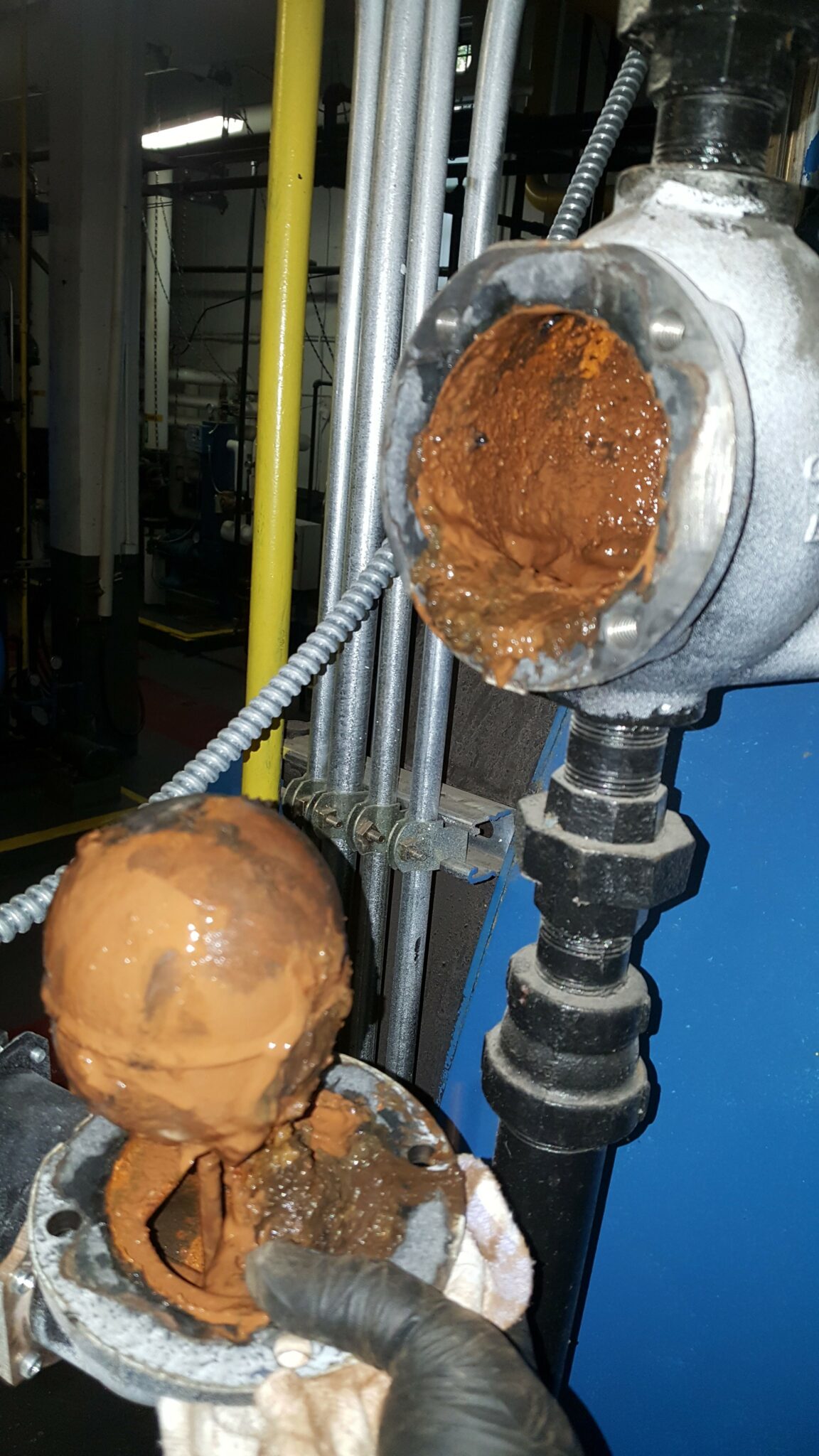

Recognizing Poor Water Quality Symptoms
Improper water chemistry causes significant damage to cast iron boilers over time. Watch for these indicators:
- Cloudy or discolored water when bleeding radiators
- Excessive sludge in drain valves
- Rapid pressure fluctuations during heating cycles
- Reduced heating efficiency despite proper thermostat settings
These symptoms suggest immediate water treatment is needed to prevent internal corrosion.
Safe Flushing Procedures Homeowners Can Perform
While complete system flushing requires professional equipment, homeowners can perform limited maintenance:
- Turn off boiler power and allow system to cool completely
- Close main water supply valve to the boiler
- Attach garden hose to drain valve, directing water to safe drainage area
- Open pressure relief valve and drain valve simultaneously
- Allow 2-3 gallons to drain before closing valves
- Refill system and verify proper pressure (12-15 PSI cold)
Never attempt to remove cast iron sections or disassemble internal components—this requires professional expertise.
Combustion Air System Maintenance
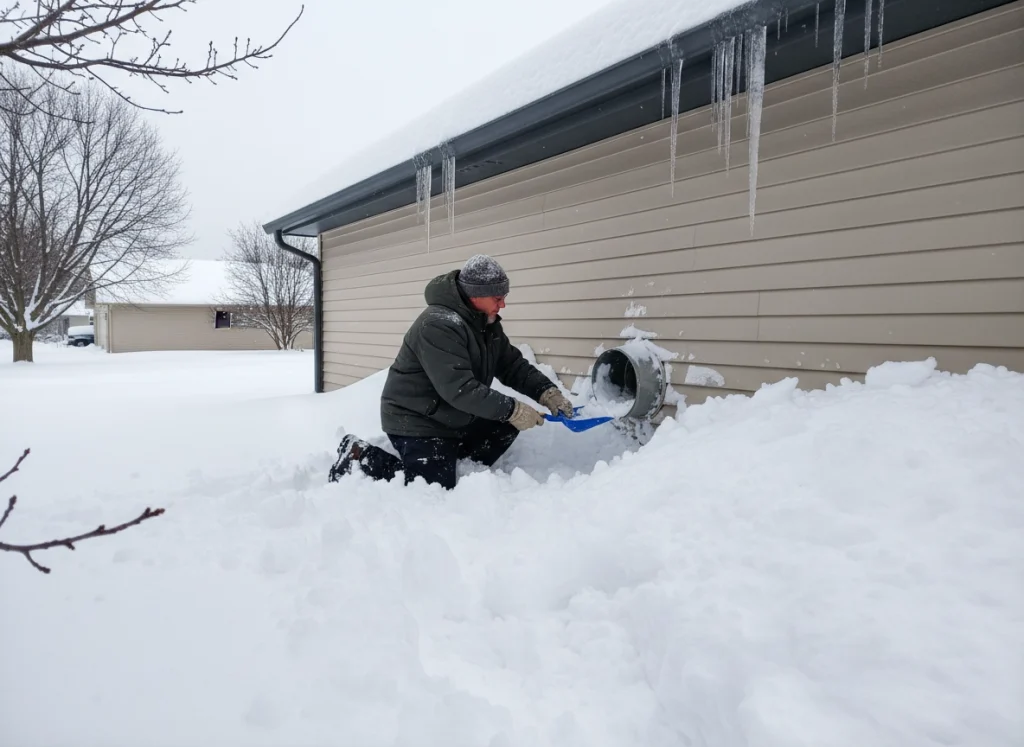

Ventilation Pathway Inspection
Your boiler requires adequate combustion air for safe operation. Check these areas quarterly:
- External air intakes for blockages from leaves, snow, or debris
- Indoor ventilation pathways for obstructions near the boiler
- Exhaust vents for proper termination away from windows or doors
Restricted airflow causes incomplete combustion, creating dangerous carbon monoxide.
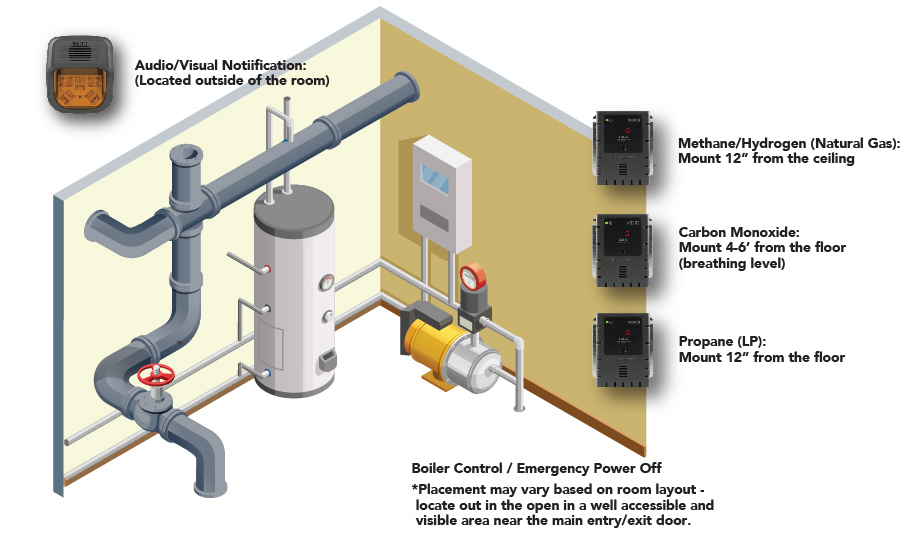
Carbon Monoxide Detector Verification
Since cast iron boilers pose carbon monoxide risks if malfunctioning:
- Install detectors within 10 feet of the boiler room
- Test detectors monthly using the test button
- Replace detectors every 5-7 years per manufacturer guidelines
- Never disable detectors during nuisance alarms—call a professional instead
Seasonal Preparation Checklist
Fall Startup Procedures
Before activating your boiler after summer:
- Visually inspect entire system for signs of summer moisture damage
- Verify all valves operate smoothly before turning on
- Check expansion tank air charge (should feel “squishy” when pressed)
- Bleed air from radiators systematically starting from top floor
- Gradually increase temperature settings over 24 hours
Rushing this process can cause thermal shock to cast iron components.
Spring Shutdown Protocol
When heating season ends:
- Schedule professional service before completely shutting down
- Maintain minimum 40°F in boiler room during freezing months
- Keep system pressurized at 12 PSI even when not in use
- Document any issues for attention before next season
Complete drainage risks corrosion from residual moisture in cast iron sections.
Troubleshooting Common Cast Iron Boiler Issues
No Heat But System Running
When your boiler operates but provides no heat:
- Check thermostat settings (batteries often die after summer)
- Verify zone valves are opening properly (listen for clicking)
- Bleed radiators to remove trapped air preventing circulation
- Inspect circulator pump for humming without movement (may need replacement)
If these steps don’t restore heat within 24 hours, call a professional.
Water Leaks Around Boiler Base
Small leaks require immediate attention:
- Tighten accessible fittings with appropriate wrench (avoid over-tightening)
- Place drip pan under leak to prevent floor damage
- Document leak rate (drops per minute) for technician assessment
- Never ignore slow leaks—cast iron can develop hairline cracks from water exposure
Safety First: When to Shut Down Immediately
Emergency Shutdown Indicators
Shut off power and gas immediately if you notice:
- Strong gas odor (rotten egg smell) near the boiler
- Visible soot around burner access panels
- Water dripping from electrical components
- Excessive condensation on flue pipes
After shutdown, ventilate the area and call your gas company or HVAC emergency service.
Proper Emergency Shutdown Procedure
- Turn off power at the dedicated circuit breaker
- Close gas supply valve (quarter-turn to perpendicular position)
- Open windows for ventilation
- Evacuate the area if gas smell persists
- Call professionals from outside the building
Never attempt to restart the system after an emergency shutdown.
Professional Maintenance Cost vs. Replacement Value
Economic Considerations for Aging Systems
Cast iron boilers often outlive their expected lifespan but require increasing maintenance:
- Under 15 years: Routine maintenance typically costs $100-$200 annually
- 15-25 years: May require $300-$500 yearly for component replacements
- Over 25 years: Repair costs often exceed 50% of replacement value
Track your maintenance expenses to determine the economic tipping point for replacement.
Recognizing End-of-Life Indicators
Consider replacement when you notice:
- Multiple hairline cracks in cast iron sections
- Frequent pressure loss requiring weekly refilling
- Consistent inefficiency despite professional servicing
- Age exceeding 30 years with major component failures
Modern condensing boilers offer 90%+ efficiency compared to 70-80% for older cast iron units.
Final Maintenance Recommendations
Consistent cast iron boiler maintenance preserves both your investment and your family’s safety. Remember that while homeowners can perform visual inspections and basic monitoring, internal components require professional expertise. Establish a relationship with a qualified HVAC technician who specializes in older boiler systems and schedule annual service before heating season begins. Document all maintenance activities and note any changes in operation between services. Most importantly, never ignore warning signs or postpone professional evaluation of potential safety issues—your cast iron boiler’s reliability depends on proactive care throughout its decades-long service life.





